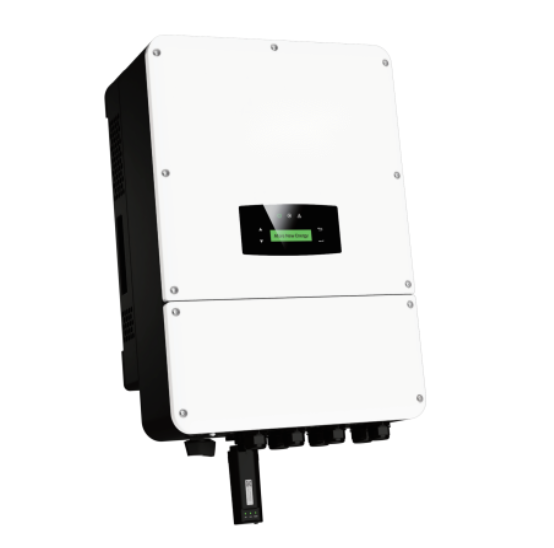
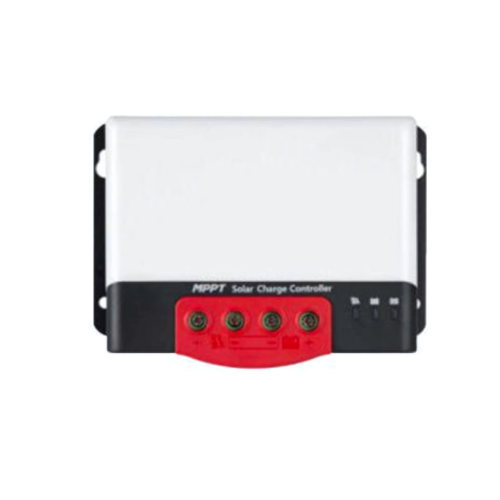
CONTROLLERS & INVERTERS
Did you know that renewable energy systems, like solar power systems, cannot function without inverters and controllers?
Inverters convert the DC electricity generated or stored by solar panels into AC electricity, making it usable for homes, businesses, and the power grid. Meanwhile, photovoltaic (PV) controllers regulate the energy from DC sources (such as solar panels) to protect batteries and ensure efficient charging.
These devices are essential for optimizing solar energy use, improving system efficiency, and ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.